fluid coupling
Large temperature Viton⢠oil seals
Welded building to remove leaks on size seven., 9.4 and 12.four
fluid coupling
Product Functions
All aluminum housing and impeller for reduced rotating inertia
Decreases vitality intake
Extensive range of mounting choices
Normal equipment coupling utilised for #imgur l[https://www.ever-power.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Fluid-Couplings.jpg]#shaft to shaft coupling
l[https://www.ever-power.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Fluid-Couplings.jpg]#shaft to shaft coupling
Fluid coupling with c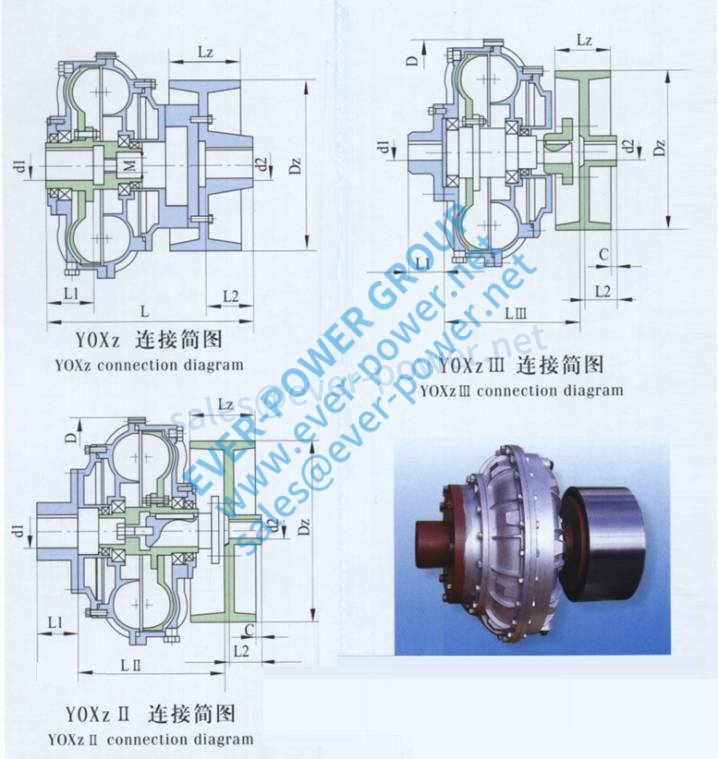 onstructed-in QD hub for sheave mounting on the electric motor shaft
onstructed-in QD hub for sheave mounting on the electric motor shaft
Fluid couplings occur common with:
These are accessible for electric motors from ½ HP to 50HP that run at speeds as lower as 500 RPM and as higher as 3600 RPM. During start-up the fluid coupling will minimize the recent draw on your electrical motor by 33%.
Fluid Couplings | Wichita Clutch
Soft Start off and/or More than Load Protection
Identified in the past as Simplatrol, Formsprag or Mesur-Fil, the more compact dimension 7., nine.four and the 12.four dimension fluid couplings are produced in China.
fluid coupling